https://ift.tt/3wAIYwZ
Dairy products are born from raw whole milk — a water-based mixture with roughly 50% of its calories coming from fat, 20% from protein, and 30-35% as net carbs (mostly from lactose).
Although this means a glass of milk is not good for keto, this doesn’t rule out every other dairy product from your low-carb lifestyle. In fact, the most popular keto ingredients are made from milk, but with one crucial difference: Most of the milk sugar is filtered out during production (and no other sugars are added in).
In this guide, we’ll show you exactly how to decipher between the best and worst keto dairy (as well as how to find out if a specific dairy product is optimal for you).
Throughout our journey into the world of keto dairy, we’ll be taking a closer look at the following topics:
- What is a dairy product exactly?
- Can you have dairy on keto?
- The worst dairy for low carb eating
- The best dairy for ketosis (including a list of the best keto cheeses)
- Dairy products you can have in moderation
- A quick overview of the best and worst keto dairy
- The benefits of keto-friendly dairy
- The potential dairy-based downsides
- Should you eat dairy on keto (or go dairy-free)?
- How much dairy should you have on keto?
- Milk and its keto-friendly substitutes
- Can you do keto without dairy?
- Key takeaways
What is a Dairy Product?
Dairy is any food product that contains or is made from milk.
However, unless you have a dairy allergy or a sensitivity to specific dairy proteins, knowing if a food is a dairy product doesn’t reveal if it is keto-friendly for you.
Uncovering the best and worst dairy for the keto diet requires us to look closer at each product’s carb content and serving size.
Is Dairy Keto-friendly: Can You Have It on the Keto Diet?

As long as the particular dairy product is low enough in carbs to fit within your daily carb limit, you can have it on keto. For most people, this limit will be around 35 grams of total carbs and 25 grams of net carbs per day.
Thus, determining if a food is “low enough” in carbs for your keto diet will depend on the other foods you eat throughout the day as well.
For example, one cup of whole milk comes with roughly 12 grams of net carbs, which is technically below the keto carb limit. However, that small glass of milk will take away nearly half of your net carbs for the day, which will make keto significantly more difficult to follow.
(This is why whole milk is often avoided on keto.)
In contrast, if you have a dairy product where the milk sugar is taken out during production, then the carb counts tend to be significantly lower. The perfect example of this is cheddar cheese and butter, which are low enough in carbs to be keto staples.
What Dairy is Not Keto-friendly? The Worst Dairy Products that Will Kick You Out of Ketosis
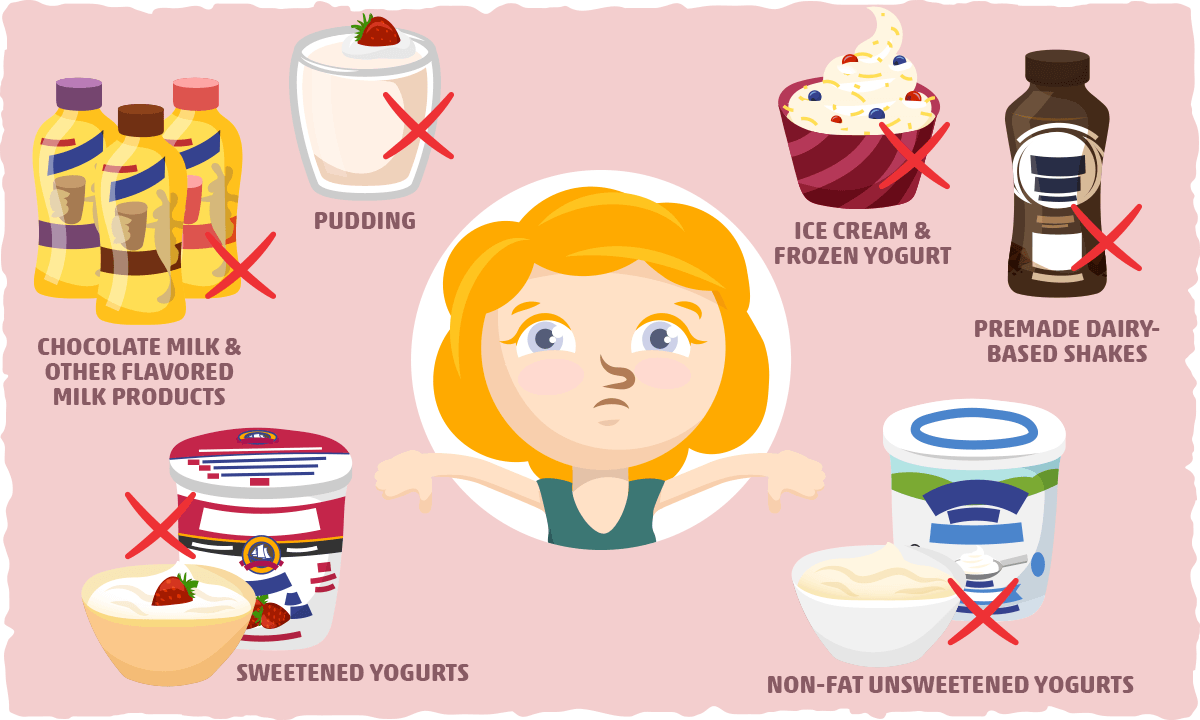
Overall, the worst dairy products for keto (and virtually every other diet) will be those that have added sugars. Not only does this cause the net carb counts to climb, but it renders the food unhealthy.
Here is a list of the most common examples of this that you’ll find in the dairy aisle:
- Sweetened yogurts — Whether the yogurt is sweetened with pure sugar or a fruit puree, skip this dairy option. This includes yogurt drinks and squeezable pouches that are marketed to kids as well.
- Non-fat unsweetened yogurt — With the fat removed, this leaves extra space for more dairy sugar on your spoon. Though these are healthier than sweetened yogurt products, non-fat plain varieties are best avoided on keto as well. Opt for full-fat unsweetened options in moderation instead.
- Chocolate milk and other flavored milk products — Sugar usually accompanies the added flavorings. In fact, most chocolate milk products have so much added sugar that we should call them “sugar milk with chocolate flavoring added.”
- Ice cream and frozen yogurt — Even the “healthier” frozen desserts are riddled with added sugars. Your best bet is making it yourself with the help of keto recipes. (Give it a try: It’s surprisingly easy.)
- Pudding — From Snack Packs to a fancy restaurant-style pudding dish, most puddings come with high amounts of sugar in every spoonful. To keep it keto-friendly, try experimenting with chia or avocado as a simple low-carb base for a quick sugar-free pudding.
- Premade dairy-based shakes — Most premade shakes, including Muscle Milk, Slim-Fast, and Ensure, are packed with added sugars. Before buying a shake for a quick meal or snack, make sure you double-check the label.
Though these products may seem vastly different, they all share a critical thread in common: Each one contains too much sugar.
Whether the sugar is from naturally occurring lactose or added during processing, these dairy options pack on the net carbs and make it nearly impossible for us to enter and sustain ketosis. Simply put, these dairy products are not keto-friendly.
If your goal is to lose weight and improve overall health, avoiding this list of foods is a great place to start (regardless of what diet you’re following).
The Best Keto Dairy: A List of High-fat, Low-carb Staples
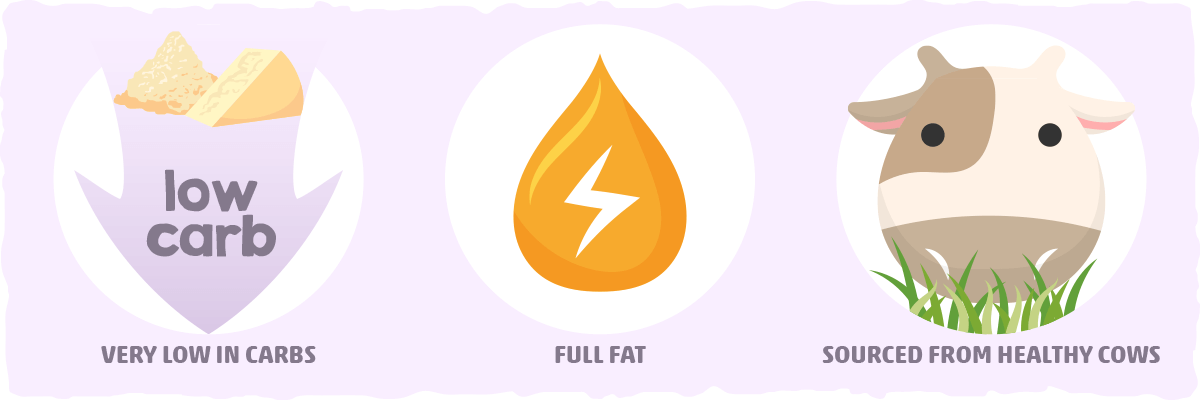
The best of the best keto dairy options will have the three following characteristics:
- Very low in carbs. In other words, most of the natural milk sugar is filtered out (by bacteria, processing, or both) and no sugar is added back in.
- Full fat. Fat-reduced and non-fat dairy products tend to be higher in carbs.
- Sourced from healthy cows. In general, these cows will be pastured-raised in a regenerative way and humanely treated.
Any dairy product with the first two qualities will be good for keto. However, the absolute best keto dairy will have all three.
List of the Best Dairy for the Keto Diet
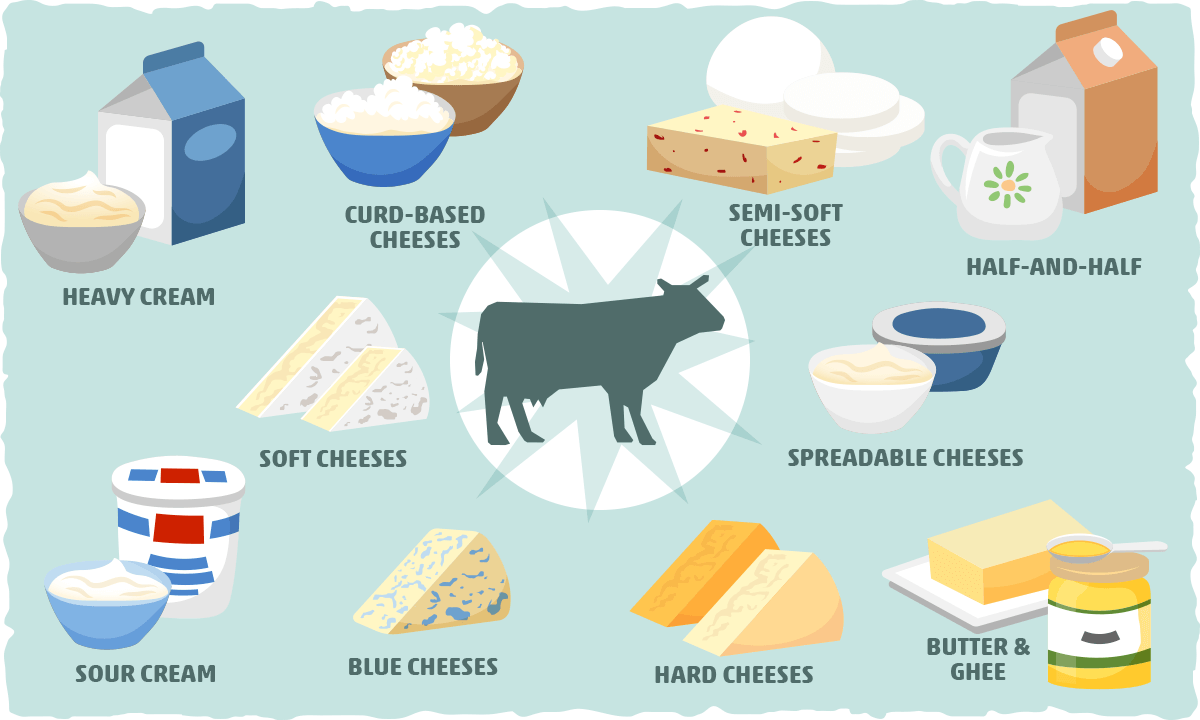
- Butter and Ghee — Butter only contains trace amounts of milk sugar, making it an excellent option for adding extra fat to your keto meal. If you’re set on having a lot of butter, make sure to get high-quality grass-fed butter, which is a healthier option for you and the cows. For those who are sensitive to any of the proteins found in dairy, ghee (also known as clarified butter) is one of the best butter replacements.
- Heavy cream — A common ingredient in keto baking and cooking, you can use heavy cream (or heavy whipping cream) to add fat to your coffee/tea, make a flavorful low carb cream sauce, or whip up your own low-carb ice cream and keto whipped cream.
- Half-and-Half — Though half-and-half is one part heavy cream with one part whole milk, you’ll only get 1 g of net carbs in every 2-tbsp serving. When buying half-and-half, make sure the ingredients are only milk and cream to ensure you have a keto-friendly dairy product.
- Spreadable cheeses — The three best keto options in this category of cheeses are cream cheese, mascarpone, and creme fraiche. You’ll find that each one is used in some of the most popular keto dessert recipes, while cream cheese serves as a great keto thickener/base for creamy soups and dips.
- Soft-ripened cheese — Brie, Camembert, and other similar soft-ripened cheeses are among the lowest in carbs of all cheeses, with roughly 0.5 gram of carb per 100 grams.
- Hard (aged) cheeses — This includes cheddar, swiss, parmesan, and provolone, which all give the good bacteria in the cheese extra time to use up the net carbs for you. Hard cheese typically contains between 2 and 4g of net carbs per 100 grams.
- Semi-soft cheese — Midway between hard and soft cheese in texture, semi-soft cheeses like mozzarella, monterey jack, feta, and havarti are versatile and widely available in the US. They have slightly more carbs than most hard cheeses, with 3.5 to 4 grams in every 100-gram serving.
- Blue cheese — Whether it is roquefort, gorgonzola, stilton, or blue cheese crumbles, this is flavorful low-carb cheese option at 2-4 grams of carbs per 100-gram serving.
- Curd-based cheeses — Treated with acid-forming bacteria and/or citric acid, milk will form curds, which is the basis of this type of cheese. The lowest carb options in this category are whole milk ricotta, full-fat cottage cheese, and paneer, with around 3-4 g in every 100g.
- Sour cream — Thanks to natural probiotics and the very low carb content of cream, sour cream only has roughly 0.3 g of carbs per tablespoon.
What Cheese is Best for Keto?
If we focus solely on the carb content in every 100-gram serving, these are the best cheeses for keto (ordered from lowest to highest in net carbs):
- Soft-ripened cheeses (brie and camembert): 0.5g
- Blue cheese: 2.4 g
- Cheddar: 2.5g
- Mascarpone and Creme Fraiche: 2.5-3g
- Whole Milk Ricotta: 3.1 g
- Parmesan: 3.2 g
- Full-fat Cottage cheese: 3.2 g
- Mozzarella and Monterey Jack: 3.6 g
- Gorgonzola: 3.6 g
- Paneer: 3.6 g
- Feta cheese: 3.9 g
- Cream cheese: 4.1g
Please note: The carbs will vary depending on the type of cheese and the brand that makes it. Double-check the label to make sure you can fit the specific product into your keto diet.

What Dairy Products Should I Limit On Keto?
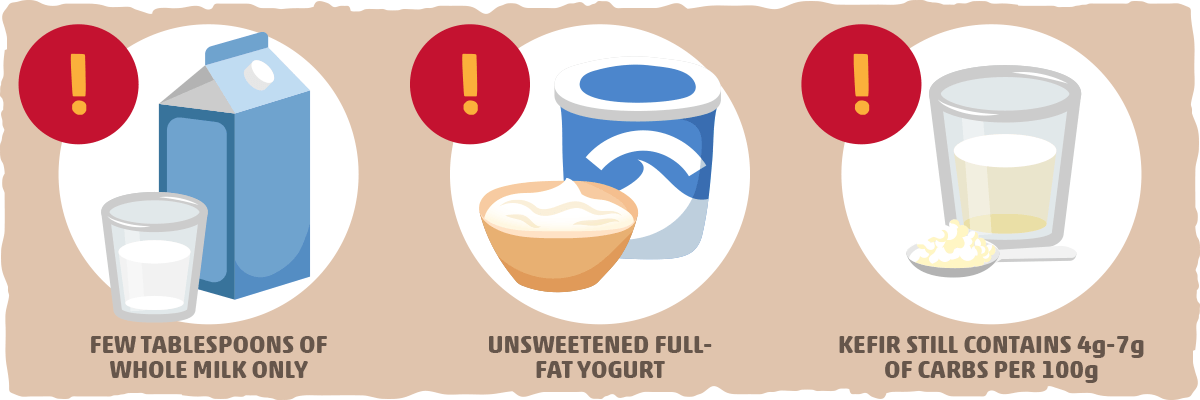
Though cheese, cream, and butter are typically the best keto dairy products, this doesn’t mean you should avoid everything else in the dairy aisle.
In fact, there are several other low-carb dairy products you can incorporate into your keto lifestyle in moderation:
- Whole milk — A glass won’t cut it on keto, but a few tablespoons can be added to recipes if needed. By the tablespoon, whole milk has only 0.8 grams of net carbs.
- Unsweetened full-fat yogurt — Though it is much healthier than sweetened yogurts, the plain variety still has some milk sugar lingering inside. This applies to greek yogurt as well, both adding around 7g of net carbs per ¾ cup serving to your keto diet.
- Kefir — This yogurt-like drink is made by controlling the souring process of milk to form a probiotic beverage. Since Kefir is at a relatively early stage of fermentation, it will tend to have more net carbs. In general, The carb content varies between 4 and 7 grams per 100 grams, depending on how it is made.
As you browse through keto recipes, you may actually find these on the ingredients list. Usually, all it takes is a small amount to provide the right texture and flavor without carb counts climbing too high.
An Overview of the Best and Worst Dairy Products for Keto
To give you a better idea of how all the above information fits together, we’ve included a chart with the net carb counts for every 100g serving of the best and worst keto dairy products for keto:

Now that we know exactly what dairy products are the best, the worst, and what should be limited on keto, let’s take a look at the benefits, the downsides, and other common dairy-related questions.
What are the Benefits of Low Carb Dairy on a Keto Diet?
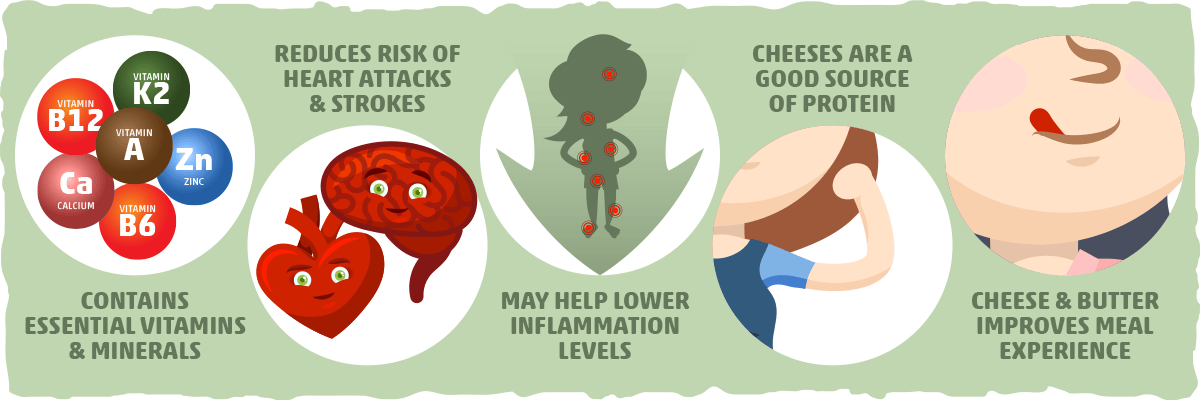
Other than the fact that keto-friendly dairy provides us with plenty of fat, it comes with several health benefits as well:
- Dairy provides us with essential vitamins and minerals. Keto dairy products have varying amounts of several key nutrients, including vitamin A, vitamin K2, vitamins B6 and B12, calcium, and zinc.
- Dairy consumption is linked to better cardiovascular health. Some studies suggest that a moderate consumption of high-fat dairy may reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Dairy intake is associated with lower inflammation levels. Though dairy products are often thought of as being inflammatory, the scientific literature points us in the opposite direction. In fact, after conducting a systematic review of 52 clinical trials, the authors of a 2017 study concluded that consuming dairy products may help lower inflammatory markers in people with metabolic diseases, such as diabetes or obesity. A more recent review from 2020 found that dairy products had neutral to beneficial effects on inflammatory markers in healthy subjects and those with metabolic disease. (That being said, dairy is likely to increase inflammation if you have a dairy allergy, lactose intolerance, or a sensitivity to specific dairy proteins.)
- Most cheeses are a good source of protein. Eating more protein, especially dairy protein, can help you feel full, build muscle, and burn more calories. Altogether, this can make fat loss easier to achieve and maintain without having to fight against increasing cravings and hunger pangs.
- Keto dairy is tasty and satisfying. Simply put, cheese and butter can turn a bland, boring meal into a 5-star culinary experience. Cheese, in particular, may also make you feel more satisfied with less food. In fact, one recent study found that cheese tends to reduce hunger and trigger the release of more “fullness hormones” than heavy cream or whipped cream.
The Potential Downsides of Keto Dairy
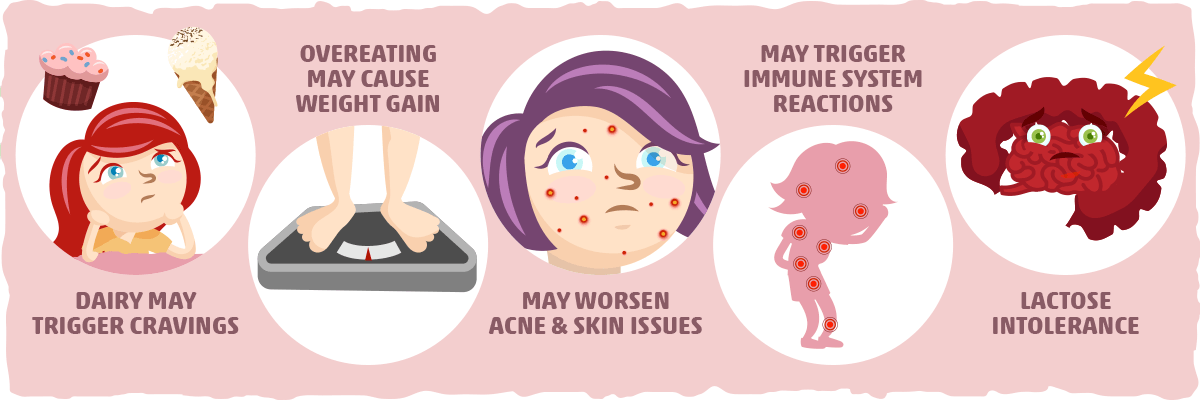
On the other side of the spectrum, dairy has a few drawbacks to look out for as well:
- Dairy may trigger cravings. Since many of us have consumed dairy alongside high-carb, highly-palatable foods throughout our lives, certain keto dairy products may trigger cravings and overeating. If this is the case for you, adding more low-carb vegetables and protein to your meals may be a better option than packing on the butter and cheese.
- Overeating keto dairy can cause weight gain. Though cheese, butter, and heavy cream are reliable keto-friendly options, don’t fall into the trap of thinking you can eat as much as you want. Unfortunately, when we overeat fat, our bodies will store it as fat. In fact, one of the most common causes of weight gain on keto is adding too much extra butter and cheese to meals. (The same applies to keto weight loss stalls as well.)
- Dairy may worsen acne and other skin issues. In some people, dairy can trigger acne flare-ups. If you notice an increase in acne after starting keto, then dairy might be the culprit.
- You might be sensitive to dairy. Certain individuals may have immune systems that overreact to dairy, which may cause digestive issues, fatigue, inflammation, or other symptoms.
- Lactose intolerance. Up to two-thirds of people worldwide are estimated to lack the enzyme necessary to digest lactose, leading to lactose intolerance. People who are lactose intolerant can usually digest low-lactose dairy products like cheese or yogurt with little to no issues. However, some may be sensitive to lactose regardless of how much they consume.
- People can develop an allergy to one or more of the proteins in milk. Although relatively common in children, a true cow’s milk allergy is rare in adults. Milk allergies can trigger digestive upset, vomiting, hives, or even anaphylaxis after consuming dairy.
How to Know if You Should Eat Dairy on a Keto or Low-carb Diet?

As is the case with other low-carb food, the response to dairy is highly individual. In general, the keto-friendly dairy products discussed above are a healthy staple of the ketogenic diet.
However, if you have a milk allergy, lactose intolerance, and/or a sensitivity to specific dairy proteins, it is best to listen to your body and either limit or avoid dairy for optimal results.
For those who are among the small subset of people with a dairy allergy, it is best to avoid all dairy products and go 100% dairy-free on keto.
If you’re lactose intolerant, you may be able to enjoy small servings of cheese, butter, and other low-lactose dairy products. That being said, anyone who finds that even tiny amounts of lactose cause digestive issues should steer clear of dairy (or at least take a lactase enzyme with dairy-containing meals).
If you’re not sure whether or not dairy is ideal for you and your keto lifestyle, consider experimenting with dairy-free keto for 3-4 weeks. While you cut out dairy, you’ll be able to figure out if low-carb dairy is triggering cravings, causing weight loss stalls, provoking acne breakouts, or causing fatigue and digestive issues.
You can also fine-tune your experiment by adding in different types of keto dairy products to see if you react negatively to one and not the other. Within a few months of experimenting, you’ll be able to figure out what dairy products are the best fit for your keto or low-carb lifestyle. (For more information on limiting dairy intake, check out our complete guide to going dairy-free.)
How Much Dairy Can You Have on Keto?
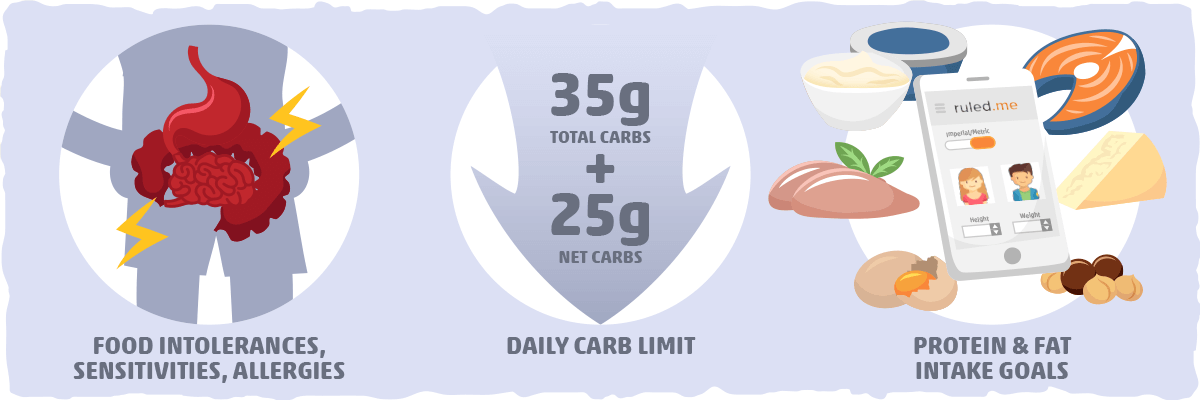
As with other keto foods, how much dairy you can eat on keto will depend on the following three factors:
- Food intolerances, sensitivities, and allergies. If you notice you feel fatigued, bloated, or gassy after a meal featuring dairy products, then you may have an issue with lactose, specific dairy proteins, or another component of that ingredient. In this case, it is best to limit or avoid dairy (as explained above).
- Your carb limit. To ensure your meal doesn’t impair ketosis (the hallmark of a ketogenic diet), you must make sure the particular food will keep you below your daily carb limit. This limit will be 35 grams of total carbs and 25 grams of net carbs per day for most people. However, if you want to find your specific carb limit, I recommend following the guidelines in our keto carb limit article.
- Your protein and fat intake goals. Even if all you eat is zero-carb dairy products, you can still gain weight if you overeat high-fat foods like cheese, butter, and cream. Though you will still be burning fat, this fat will come exclusively from the food you eat and not your stored belly fat. Along with optimizing your fat intake, eating the right amount of protein is crucial for getting the results you want as well. If you’d like to find out how much protein and fat you should aim to eat each day, plug your info into our keto calculator.
What About Milk Alternatives for Keto? Finding the Best Dairy-based and Dairy-free Options
Keto-friendly milk alternatives can come with the same issues as other dairy products, particularly regarding high levels of natural sugar and added sugar. Because of this, searching for the right low-carb milk substitute can be time-consuming.
To save you time and money, I highly recommend reading through our guide to keto milk substitutes. Not only will you find dairy-free keto milk you can drink by the cup, but you’ll learn about the perfect alternatives for your favorite dairy-based recipes.
Can You Do Keto Without Dairy?
Though low-carb dairy is one of the most common keto ingredients, this doesn’t mean that you must include it in your keto lifestyle.
In fact, you can make a keto-friendly dairy-free version of virtually any dairy-based food with the right recipes and substitutes. For example, you can easily make a keto coconut cream yogurt or a sugar-free chocolate shake. (You can keep low-carb crepes and chocolate silk pie on your keto menu as well.)
For more dairy-free recipes, replacements, and tips, read through our comprehensive guide to the dairy-free ketogenic diet.
Key Takeaways — The Best and Worst Dairy for Your Keto Diet
Dairy follows the same rules as any other food on keto. More specifically, the best keto dairy will have the following characteristics:
- Very low in carbs
- High in fat (and can be a good source of protein as well)
- Comes from a high-quality source. In this case, the dairy should come from healthy cows (pasture-raised and humanely treated, using regenerative methods).
This is why the top three dairy products you’ll find in keto recipes and food lists are heavy cream, butter, and cheese. Each one contains only a small amount of natural milk sugars and provides us with a great source of fat. (All that’s left is making sure they are made from high-quality milk.)
In contrast, the worst keto dairy products will contain added sugars (and will usually have a reduced fat content as well). The most popular examples of this are flavored milks and yogurts, such as fruit-at-the-bottom yogurt, squeezable yogurts, yogurt drinks, and chocolate milk.
That being said, even if you only have zero-carb dairy products, it is still possible to overeat them, gain fat, and impair health. This is why it is crucial to keep your food intake within your daily macro goals to get the results you expect from keto.
The easiest way to do this is by using the Ruled.me keto app to calculate your macro goals and personalize a daily meal plan for you.
Please note: For those of you who’d like to go 100% dairy-free or experiment with dairy-free keto dieting, make sure to read our dairy-free keto guide first.
Sources
- Association of dairy intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 21 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study — The Lancet
- Effects of Full-Fat and Fermented Dairy Products on Cardiometabolic Disease: Food Is More Than the Sum of Its Parts — NCBI
- Dairy products and inflammation: A review of the clinical evidence — NCBI
- The Effects of Dairy Product and Dairy Protein Intake on Inflammation: A Systematic Review of the Literature — Journal of the American College of Nutrition
- Dairy products influence gut hormone secretion and appetite differently: A randomized controlled crossover trial — NCBI
- The Dairy Free Keto Diet Guide — Ruled.me
- Ketogenic Diet Food List: Everything You Need to Know — Ruled.me
- Can the Ketogenic Diet Improve Acne? — Ruled.me
- Food allergies and food intolerances — Harvard Health
The post Dairy & Keto: Best, Worst, and Substitutes appeared first on Ruled Me.
https://ift.tt/3rXu94a
via Ruled Me https://www.ruled.me
April 7, 2021 at 11:44AM
0 Comments